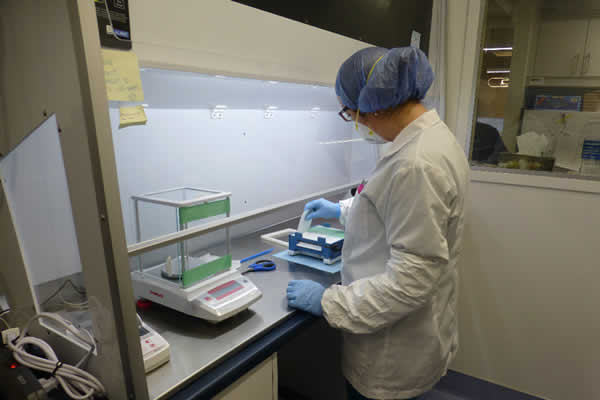
Compounding Pharmacy
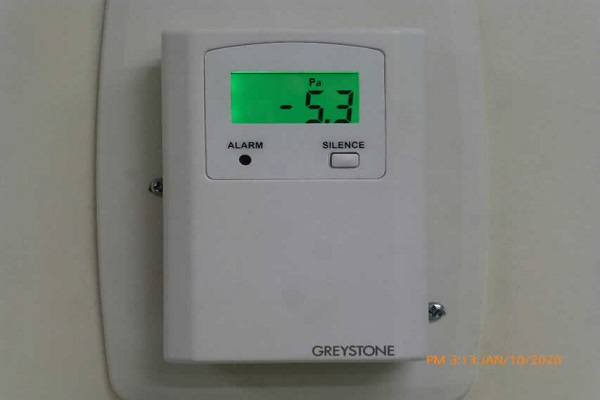
Zone Pressurization
- Service: Mechanical
- Location: Alberta (various locations)
- Multiple Pressure Gradients Achieved
Project Summary
Multiple pressure gradients were achieved between zones.
Compounding Rooms are used in pharmacies to create specialized, individualized medications by mixing pharmacy drugs in specific ratios as required by the patient.
The NAPRA Guidance model specifies the updated requirements for the compounding of non-sterile preparations. Such preparations are to be conducted in NSHD (Non-sterile Hazardous) rooms which are called Level C rooms. Level C rooms need a minimum of 12 ACH of continuous ventilation and a minimum negative pressure of 2.5 Pa relative to surrounding rooms. Level C rooms should not be contiguous with the general pharmacy area but should be separated from the general pharmacy area by a buffer zone called a Level B room. Level B rooms need to be well-ventilated with ideally 6 ACH and neutral pressurization.
All compounding in Level C rooms are to be conducted in a containment device/ fume hood (CPEC – Containment Primary Engineering Control). The fume hoods can draw air from the room and recirculate it back into the room after double HEPA filtration.
The Level C (C-SEC) room serves as a secondary containment unit for the compounding activities.
The air from level C rooms cannot be recirculated in the general pharmacy and should be duly exhausted after a single level of HEPA filtration.
We designed multiple compounding rooms with a negative pressurization of -12.5 Pa ( 5x requirement) and 20 ACH for the Level C Areas and 8 ACH for the Level B areas. Our challenge was to provide enough air flow to a buffer room which acted as a gateway to a Level C (Hazardous room with negative pressurization) and an ISO 8 Clean room (Positive pressurization of +25 Pa) with an interstitial ante room(with a positive pressurization +12.5Pa) in between the buffer and the ISO 8 room. The task was achieved with a 5 ton system. The hazardous room was ventilated using an exhaust fan (825 cfm @ 1.5″ ESP).
References: CSA Z317.2 Special requirements for heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems in health care facilities; ASHRAE 170 Ventilation of Health Care Facilities, ASHRAE 62.1 Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality; HEPA High-Efficiency Particulate Air; NAPRA Guidance Document for Pharmacy Compounding of Non-sterile Preparations


Recent Posts

Ways to Improve Your Indoor Air Quality and Energy Efficiency – HRV or ERV
Ways to Improve Your Indoor Air Quality and Energy Efficiency – HRV or ERV If you want to improve the indoor air quality and energy

HVAC Energy Saving Products
HVAC Energy Saving Products In today’s energy-conscious world, it is crucial to optimize HVAC systems for efficiency and cost savings. Lexus Engineering can help you

Introduction to the HeatSavr Liquid Pool Cover
Introduction to the HeatSavr Liquid Pool Cover HeatSavr is an innovative liquid pool cover solution that helps conserve energy, reduce water evaporation, and maintain optimal

Endotherm, a Revolutionary but Simple Additive is an Energy Savings Leader
Endotherm, a Revolutionary but Simple Additive is an Energy Savings Leader Endotherm can revolutionize your heating or cooling system with its advanced formula. It enhances

Discover the Power of Efficiency: Uncovering Savings With an Energy Audit
Discover the Power of Efficiency: Uncovering Savings With an Energy Audit Are you and your business looking for ways to save money and enhance
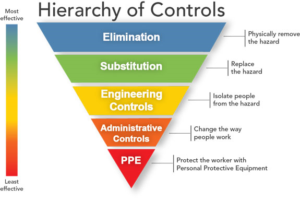
Hierarchy of Controls
There is a popular misconception that PPE is the most effective way of controlling exposures, but Engineering Controls are more effective. Overview Controlling exposures to
Contact Details
![]()
Headquarters:
Unit 208, 8716-48 Avenue NW
Edmonton, Alberta
T6E 5L1


